参考资料:C++ Primer(5th Edition)
C++、IO库
-
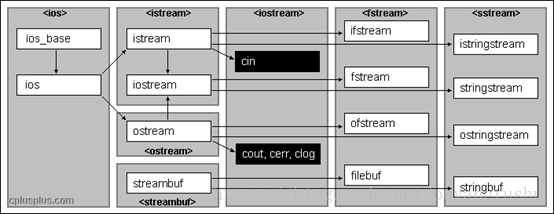
istream, wistream 从流读取数据;
- ostream, ostream 向流写入数据;
- iostream, wiostream 读写流;
- ifstream, wifstream 从文件读取数据;
- ofstream, wofstream 向文件写入数据;
-
fstream, wfstream 读写文件
- getline 从一个给定的istream读取一行数据,存入一个给定的string对象中。
- istringstream, wistringstream从string读取数据
- ostringstream, wostringstream从string写入数据
- stringstream, wstringstream 读写stream
以w开头的类是为了支持宽字符如wchar_t而设计的。类之间差异可以忽略,这是通过继承机制实现的。如ifstram和istringstream都继承自istream。
注意,IO对象无拷贝或者赋值。
只有当一个流处于无错误状态,才能写入数据。一般把它当一个条件使用:
while(cin>>word)
我们知道endl, 它到底是什么呢?
endl 完成换行并刷新缓冲区。每个输出流都管理一个缓冲区,只有缓冲区刷新,数据才会真正写到设备或者文件。
flush:
cout<<"s"<<flush;//输出s然后刷新缓冲区,不附加任何额外字符。
ends:
输出”s”和一个空字符,然后刷新缓冲区。
文件输入输出
ifstream 可以从一个给定文件进行读操作。
ofstream 可以对一个给定文件进行写。
fstream 可以读写文件。
fstream f;
fstream f(s,mode);//s为文件名,mode为模式
基本操作:
f.open(s);//打开指定文件
f.close();//关闭文件
f.is_open();//返回bool值,与f关联的文件是否成功打开且尚未关闭
下面介绍模式mode
- in 以读方式打开,只可以用ifstream::in 或 fstream::in
- out 以写的方式打开,只可以用ofstream:out或fstream::out
- app 每次写操作前均定位到文件末尾
- ate 打开文件后立即定位到文件末尾
- trunc 截断文件,只有out也被设定时,才可设定trunc模式
- binary 以二进制的形式进行操作
示例代码:
ofstream out;
ifstream in ;
fstream inout;
out.open("out.txt",ios::app|ios::out );
in.open("test.txt",ios::in|ios::binary);
inout.open("a.txt",ios::app|ios::binary|ios::out|ios::in);
out<<"Hello"<<endl;
vector<string> mybuff;
if(!in.is_open())
{
cerr<<"Error opening file";exit(1);
}
char buff[256];
while(!in.eof())
{
in.getline(buff,100);
mybuff.push_back(buff);
}
in.close();
out.close();
inout.close();
文件位置指针
1) tellg() 和tellp()
这两个成员函数不用传入参数,返回pos_type 类型的值(根据ANSI-C++标准) ,就是一个整数,代表当前get流指针的位置 (用tellg—–ifstream) 或 put 流指针的位置(用tellp—–ostream).
2)seekg() 和seekp()
这对函数分别用来改变流指针get 和put的位置。两个函数都被重载为两种不同的原型:
seekg ( pos_type position ); seekp ( pos_type position );
使用这个原型,流指针被改变为指向从文件开始计算的一个绝对位置。要求传入的参数类型与函数 tellg 和tellp 的返回值类型相同。
seekg ( off_type offset,seekdir direction );—–ifstream seekp ( off_type offset, seekdir direction );—–ostream
使用这个原型可以指定由参数direction决定的一个具体的指针开始计算的一个位移(offset)。它可以是:
| ios::beg | 从流开始位置计算的位移 |
|---|---|
| ios::cur | 从流指针当前位置开始计算的位移 |
| ios::end | 从流末尾处开始计算的位移 |
int main() {
std::ifstream fileObject;
fileObject.open("test.txt", std::ios::out | std::ios::binary);
int n = 10;
// 定位到 fileObject 的第 n 个字节(假设是 ios::beg)
fileObject.seekg(n);
// 把文件的读指针从 fileObject 当前位置向后移 n 个字节
fileObject.seekg(n,std::ios::cur);
// 把文件的读指针从 fileObject 末尾往回移 n 个字节
fileObject.seekg(n,std::ios::end);
// 定位到 fileObject 的末尾
fileObject.seekg(0,std::ios::end);
return 0;
}
Eg 2:
// obtaining file size 二进制
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
constchar * filename = "test.txt";
int main() {
long l, m;
std::ifstream in(filename, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
l= in.tellg();
in.seekg(0,std::ios::end);
m= in.tellg();
in.close();
std::cout<<"size of "<< filename;
std::cout<<" is "<< (m - l) <<" bytes.\n";
return 0;
}